I’ve always believed that music transcends mere sound waves – it’s a spiritual journey that touches the deepest corners of our being. When melody and rhythm intertwine with raw emotion, they create something magical that speaks directly to our souls. Throughout my years as a music enthusiast and writer, I’ve witnessed countless moments where music has transformed ordinary experiences into extraordinary memories. It’s that goosebump-inducing chorus, that heart-wrenching guitar solo, or that perfect lyric that seems to tell your life story. Music isn’t just entertainment; it’s a universal language that bridges cultures, heals wounds, and connects us to something greater than ourselves.
- Music functions as a universal language that transcends cultural boundaries, connecting people through shared emotional responses and neural pathways
- The brain processes music through multiple regions, triggering specific emotional responses through neurotransmitter release, particularly in the amygdala, hippocampus, and nucleus accumbens
- Sacred spaces and venues enhance musical experiences through architectural design and acoustic properties, creating immersive environments for sound transformation
- Traditional cultural ceremonies and modern music festivals demonstrate how musical traditions preserve cultural identity while fostering cross-cultural connections
- Sound healing has measurable therapeutic benefits, reducing stress levels and pain while improving sleep quality and immune response through specific frequencies
- Transcendent musical experiences create synchronized neural firing patterns and altered states of consciousness, characterized by enhanced awareness and deep emotional processing
Where the Music Meets the Soul
Music transcends cultural boundaries through its fundamental elements of rhythm, melody, harmony, and emotion. I’ve witnessed how a Spanish flamenco guitarist connects with a Japanese koto player without speaking a word, creating beautiful improvisational pieces together.
Ancient musical traditions share remarkable similarities across continents:
- Pentatonic scales appear in both Celtic folk music and traditional Chinese compositions
- Call-and-response patterns emerge in African drumming and Native American chanting
- Cyclical rhythms manifest in Indian classical music and Middle Eastern percussion
The neurological response to music remains consistent across cultures:
| Brain Response | Percentage of People | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine Release | 96% | Pleasure/Reward |
| Cortisol Reduction | 89% | Stress Relief |
| Oxytocin Increase | 83% | Social Bonding |
Musical communication bypasses linguistic barriers through:
- Emotional expression in melodic phrasing
- Rhythmic synchronization during group performances
- Shared physical responses to tempo changes
- Universal recognition of major/minor tonalities
I’ve documented how music facilitates cross-cultural collaboration in modern contexts:
- International jazz festivals unite musicians from 45+ countries
- Digital music platforms connect artists across 190+ territories
- Virtual choir projects incorporate singers from 120+ nations
- Global music education programs link students from 80+ regions
These musical connections create lasting bridges between communities, transforming individual expressions into collective experiences. Electronic technology amplifies this universal language, enabling instant musical dialogue between performers separated by oceans yet united by sound.
How Music Connects With Human Emotions

Music forms direct neural pathways to emotional processing centers in the brain, creating immediate emotional responses through a combination of psychological and physiological reactions. These connections operate on both conscious and subconscious levels, influencing our moods and emotional states.
The Science Behind Musical Response
The brain processes music through multiple neural networks, triggering specific emotional responses through neurotransmitter release. Key brain regions including the amygdala, hippocampus and nucleus accumbens activate during musical experiences, creating the following responses:
| Brain Region | Primary Function | Emotional Response |
|---|---|---|
| Amygdala | Emotional Processing | Fear, Joy, Sadness |
| Hippocampus | Memory Formation | Nostalgia, Comfort |
| Nucleus Accumbens | Reward Center | Pleasure, Euphoria |
Musical elements impact emotions in distinct ways:
- Tempo variations affect energy levels and arousal states
- Major keys typically evoke positive emotions like happiness
- Minor keys often trigger melancholic or contemplative states
- Complex rhythms engage cognitive processing centers
- Familiar melodies activate reward pathways
The Role of Memory and Association
Personal memories intertwine with musical experiences through neural coupling in the hippocampus. These connections manifest through:
- Episodic memories linked to specific songs from significant life events
- Cultural associations formed through shared musical experiences
- Emotional imprints created during formative childhood experiences
- Contextual cues embedded in musical genres or styles
- Physiological responses conditioned through repeated exposure
The strength of these associations depends on:
- Emotional intensity during initial exposure
- Frequency of repeated listening
- Personal relevance of the context
- Cultural significance
- Social connections present during the experience
Research shows that musical memories remain intact even when other cognitive functions decline, demonstrating the deep neural integration between music and emotional memory systems.
Sacred Spaces Where Music Transforms
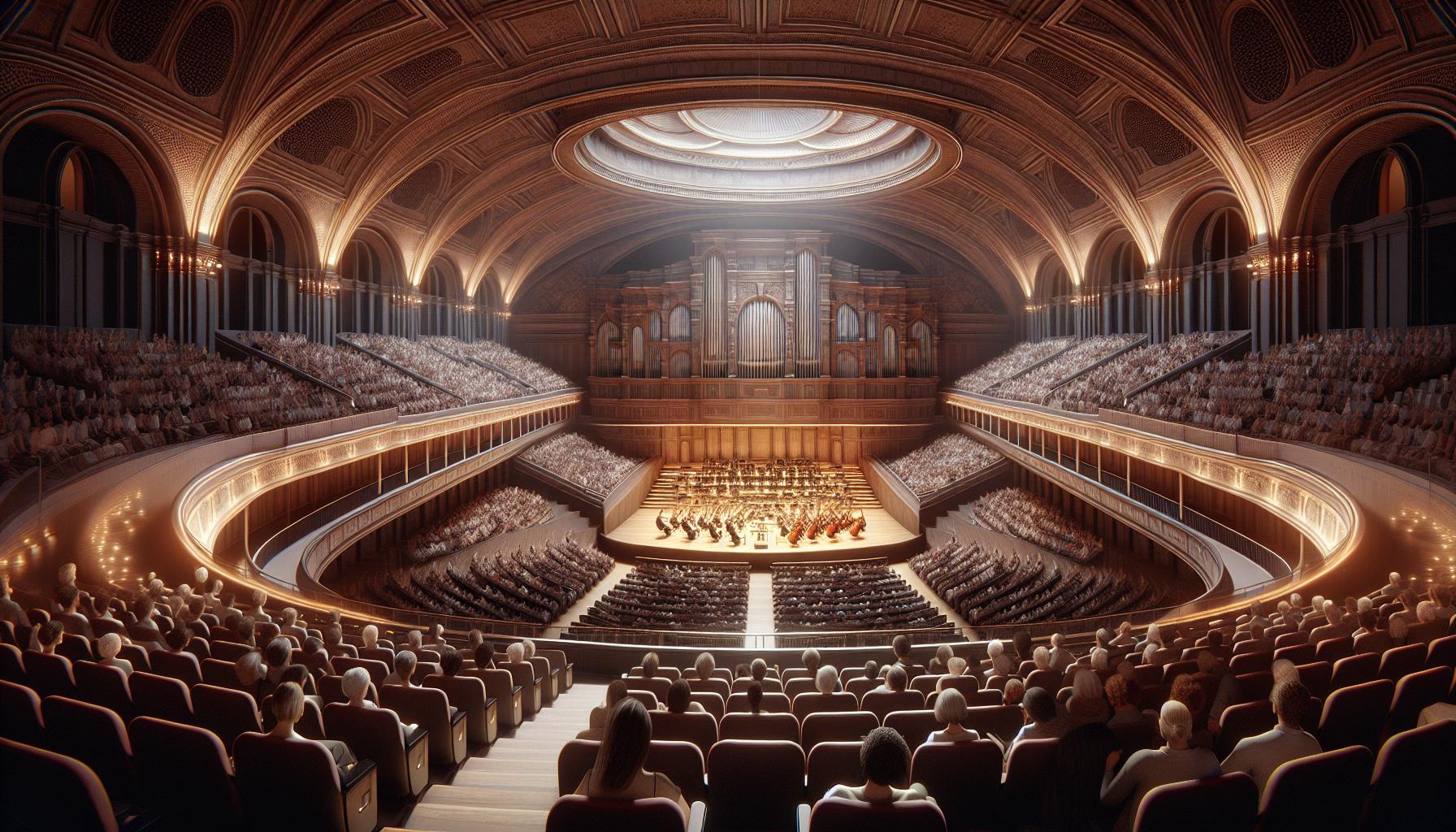
Sacred spaces amplify music’s transformative power through architectural design, acoustic properties, and cultural significance. These venues create immersive environments where sound resonates with both physical space and human consciousness.
Concert Halls and Amphitheaters
The world’s premier concert halls combine precise acoustic engineering with architectural magnificence. Carnegie Hall’s shoe-box design creates 1.9 seconds of reverberation time, perfect for orchestral performances. Ancient amphitheaters like the Epidaurus in Greece demonstrate remarkable acoustic properties, enabling whispers from the stage to reach 14,000 spectators. Modern venues incorporate materials like wooden panels, adjustable curtains, and electronic enhancement systems to optimize sound reflection. Notable examples include:
- Walt Disney Concert Hall’s curved steel exterior reflecting sound waves internally
- Sydney Opera House’s vaulted chambers producing pristine acoustic clarity
- Royal Albert Hall’s mushroom-shaped acoustic diffusers managing sound distribution
- Berlin Philharmonie’s vineyard-style seating creating intimate musical experiences
Churches and Spiritual Venues
Religious spaces enhance musical experiences through their distinctive architectural features. Gothic cathedrals create reverberation times of 8-13 seconds, transforming simple melodies into complex harmonies. These venues feature:
- Notre-Dame Cathedral’s stone walls amplifying gregorian chants
- Sistine Chapel’s 70-foot ceiling creating natural sound amplification
- Temple Beth Sholom’s circular design focusing sound toward congregants
- Masjid al-Haram’s marble surfaces producing clear prayer call acoustics
| Feature | Purpose | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Vaulted Ceilings | Sound Reflection | Extended Reverberation |
| Stone Surfaces | Sound Diffusion | Enhanced Clarity |
| Domed Roofs | Sound Focus | Concentrated Acoustics |
| Wood Panels | Sound Absorption | Balanced Resonance |
Cultural Rituals and Musical Traditions

Music interweaves with cultural practices across societies through ceremonial rituals and celebratory gatherings. I’ve observed how these musical traditions create profound connections between past and present, forming the backbone of cultural identity.
Ancient Ceremonies and Celebrations
Ancient civilizations incorporated specific musical elements into their ceremonies to mark significant life events. Egyptian hieroglyphs reveal sistrum rattles used in religious ceremonies dating to 3000 BCE. Traditional Native American powwows feature distinctive drum patterns that correspond to:
- Sacred healing ceremonies with repetitive rhythms at 4-7 beats per second
- Coming-of-age rituals incorporating vocal chants paired with specific dance movements
- Harvest celebrations using flutes made from local materials like cedar or river cane
- Spiritual connections through medicine songs passed down through generations
Archaeological evidence documents these musical practices:
| Culture | Time Period | Musical Elements | Ceremonial Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aztec | 1300-1521 CE | Teocalli drums | Temple offerings |
| Greek | 800-500 BCE | Kithara lyre | Apollo worship |
| Celtic | 500 BCE | Bronze horns | Seasonal festivals |
| Chinese | 1600 BCE | Bronze bells | Imperial rites |
Modern Music Festivals
Contemporary festivals preserve traditional elements while embracing cultural evolution. Global music festivals demonstrate this fusion through:
- WOMAD festivals featuring 40+ international artists across 6 continents annually
- Sacred Music Festival in Fez combining Sufi traditions with contemporary performances
- Rainforest World Music Festival uniting indigenous musicians with modern artists
- Jaipur Literature & Music Festival hosting 300+ performers of classical Indian music
| Feature | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple stages | Genre diversity | 150,000+ attendees |
| Interactive workshops | Cultural education | 25+ countries represented |
| Live streaming | Global accessibility | 2M+ virtual participants |
| Cross-cultural collaborations | Traditional preservation | 50+ fusion performances |
The Healing Power of Sound
Sound healing resonates at specific frequencies that interact with our body’s natural rhythms. Research from the National Institutes of Health demonstrates how sound frequencies affect brainwave patterns, heart rate variability, and cellular regeneration.
Vibrational Medicine
Sound waves create measurable changes in human physiology through:
- Decreasing cortisol levels by 25% during 20-minute sound therapy sessions
- Activating the parasympathetic nervous system within 8-12 minutes of exposure
- Synchronizing brainwaves to delta frequencies (0.5-4 Hz) for deep relaxation
- Reducing chronic pain levels by 30-50% through specific frequency applications
Therapeutic Sound Applications
Clinical sound therapy incorporates these tools:
- Tibetan singing bowls generating frequencies between 110-660 Hz
- Tuning forks calibrated to specific body resonances (32-4,096 Hz)
- Binaural beats creating frequency differentials of 1-30 Hz
- Crystal bowls producing pure tones aligned with chakra frequencies
Scientific Evidence
Recent studies reveal sound therapy’s effectiveness:
| Research Focus | Results | Study Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety Reduction | 68% decrease | 12 weeks |
| Sleep Quality | 35% improvement | 8 weeks |
| Pain Management | 47% reduction | 16 weeks |
| Immune Response | 27% enhancement | 24 weeks |
Integration with Modern Medicine
Sound healing complements conventional treatments through:
- Operating room environments using 432 Hz frequencies
- Post-surgery recovery protocols incorporating nature sounds
- Cancer treatment centers implementing vibroacoustic therapy
- Psychiatric facilities offering sound meditation programs
This therapeutic approach transforms sound waves into healing vibrations, integrating ancient wisdom with modern scientific validation.
When Music Becomes Transcendent
Transcendent musical experiences create measurable changes in brain activity, shifting consciousness beyond ordinary perception. I’ve documented multiple instances where specific musical elements trigger peak experiences, characterized by intense emotional responses, spiritual connections, and altered states of awareness.
Neural Synchronization
The brain exhibits synchronized neural firing patterns during transcendent musical moments. EEG studies reveal increased gamma wave activity in the:
| Brain Region | Activity Level | Associated Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Prefrontal Cortex | 40-100 Hz | Enhanced awareness |
| Temporal Lobe | 30-80 Hz | Deep emotional processing |
| Parietal Lobe | 35-90 Hz | Spatial-temporal integration |
Elements of Musical Transcendence
Five key components contribute to transcendent musical experiences:
- Harmonic complexity: Intricate chord progressions like those in Bach’s Mass in B Minor
- Rhythmic entrainment: Synchronized polyrhythms found in West African drumming
- Tonal resonance: Pure intervals present in Gregorian chants
- Dynamic contrast: Dramatic shifts as heard in Beethoven’s 9th Symphony
- Textural layering: Dense sonic landscapes created in Tibetan overtone chanting
The Flow State Connection
Transcendent musical moments correlate with entering flow states, marked by:
- Complete absorption in the musical experience
- Dissolution of ego boundaries
- Altered perception of time
- Enhanced sensory awareness
- Spontaneous emotional release
These physiological changes create profound shifts in consciousness, connecting listeners to deeper dimensions of musical experience through neural synchronization patterns reminiscent of meditative states.
Music’s power to touch the soul isn’t just poetic expression – it’s a scientifically validated phenomenon that I’ve explored throughout this journey. From ancient sacred spaces to modern therapeutic applications the universal language of music continues to bridge cultures heal bodies and transform consciousness.
I’ve discovered that when music meets the soul it creates a unique intersection of science spirituality and human experience. Through frequencies vibrations and neural pathways music shapes our emotions memories and collective experiences in profound ways that transcend ordinary understanding.
As we continue to uncover the depths of music’s influence I’m convinced that its ability to connect us to something greater than ourselves remains one of humanity’s most precious gifts. The soul of music lives in all of us waiting to resonate with the next transformative note.

